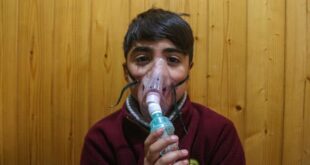
Health officials in the U.K. are warning the public about a concerning rise in whooping cough after cases soared 250% this year.
Between July and November, there were 716 reported cases of pertussis, a bacterial infection of the lungs, which is three times higher than the same period in 2022, the U.K.’s Independent reported, citing the U.K. Health Security Agency (UKHSA).
Dr Gayatri Amirthalingam, Deputy Director of Public Health Programmes at the agency, said the number of infections had decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic due to social distancing and lockdown policies, but is now on the rise again, according to the report.
Another expert, Professor Beate Kampmann, of the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, told The Sun, “The rise in cases might be because of missed vaccination appointments, possibly during the pandemic.”
HOW TO PROTECT YOUR CHILD FROM WHOOPING COUGH

The U.K. government has reported an alarming 250% increase in whooping cough cases. (iStock | National Institutes of Health)
“Severe disease is almost entirely preventable if the mother is vaccinated in pregnancy and her protective antibody reach the baby through the placenta and protect until the baby gets its own vaccines,” said Kampmann.
“It is therefore important that everyone looks at their vaccination records to check if they might have missed this vaccine, which is given with the routine childhood immunizations and in pregnancy.”
Pertussis, also called whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory disease that can cause serious illness, especially in babies and children. It is known for uncontrollable, violent coughing that can make it difficult to breathe, according to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
In severe cases, intense coughing can lead to vomiting and sore or even fractured ribs. After fits of many coughs, an infected person may need to take deep breaths, which results in the “whooping” sound the disease is named for. Another name for the disease is the 100-day cough, because it may last for several weeks or months, the U.K. National Health Service (NHS) says.
CDC’S COMMENTS ON TODAY’S PNEUMONIA OUTBREAKS VS. THE EARLY COVID CASES, AS COMPARED BY EXPERTS
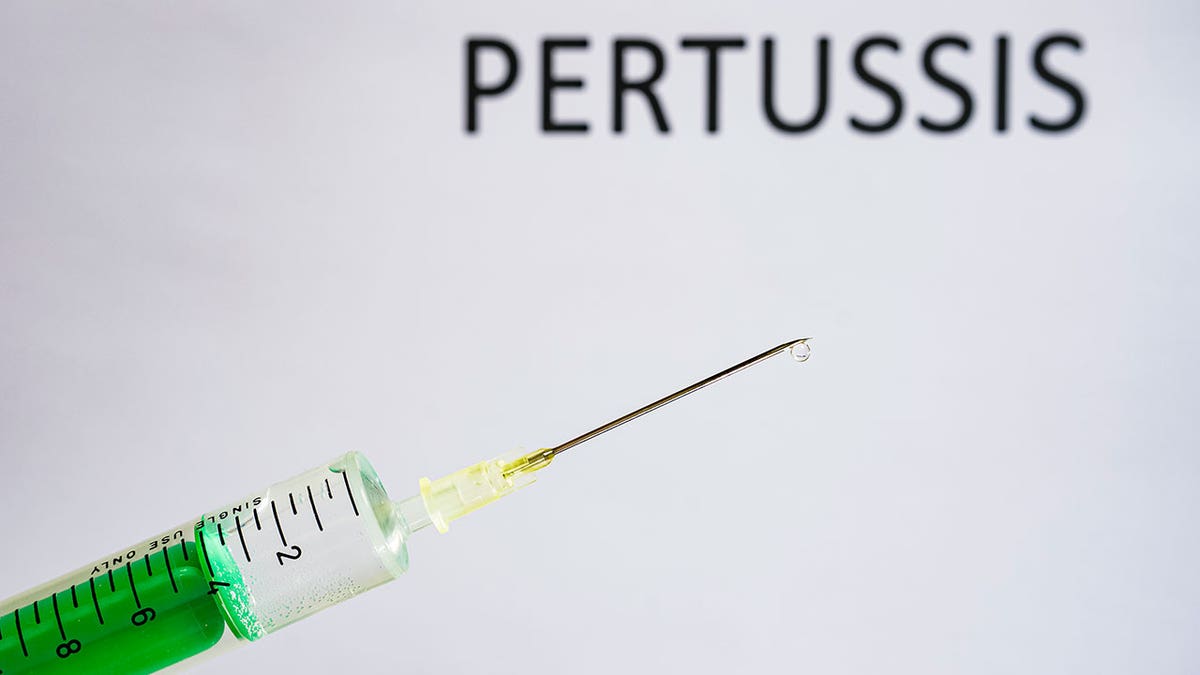
Whooping cough is easily preventable, and a vaccine is available that protects babies and children. (Frank Bienewald/LightRocket via Getty Images)
The NHS notes whooping cough is easily preventable, and a vaccine is available that protects babies and children.
However, U.K. government data shows that vaccine rates for pertussis have fallen to their lowest level in seven years.
In 2022, there was an average vaccine uptake of 61.5% in England, a decrease of 3.9% since 2021 and 7.6% from 2020, The Sun reported.
The NHS urges parents to schedule a doctor’s appointment if they or their child develop symptoms of whooping cough, or have a cold for more than three weeks that is getting worse.
CHILDREN’S PNEUMONIA OUTBREAK, ‘LIFE-CHANGING’ FAT DISORDER SURGERY, AND 2024 HEALTH PREDICTIONS

Another name for the disease is the 100-day cough, because it may last for several weeks or months, according to the U.K. National Health Service. (Mike Kemp/In Pictures via Getty Images)
Treatment for the disease depends on the patient’s age and how long they’ve had the infection. Severe cases may require hospital treatment for babies under 6 months old.
If pertussis is diagnosed within three weeks of infection, the patient will be given antibiotics to fight the illness and prevent its spread to others, the NHS says.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Those who have had whooping cough for more than 3 weeks are no longer contagious and do not need antibiotics.
For more Health articles, visit foxnews.com/health.

 Latest Breaking News Online News Portal
Latest Breaking News Online News Portal